Redux 必要条件
The Redux core library is available as a package on NPM for use with a module bundler or in a Node application:
# NPM
npm install redux
# Yarn
yarn add reduxredux理解
什么: redux是专门做状态管理的独立第3方库, 不是react插件
作用: 对应用中状态进行集中式的管理(写/读)
开发: 与react-redux, redux-thunk等插件配合使用
类比图书馆借书流程:
- 首先,我们要借一本书,
- 借书的人(React Components),他说‘我要借一本书’(actionCreaters)
- 这句话被图书馆管理员(store)听见后,管理员去找这本书,但是他自己记不住
- 于是管理员去查阅图书记录本(reducers),记录本会显示这本书放在哪(一来一回)
- 管理员(store)知道这本书放在哪,找到这本书,把这本书给借书的人(React Components)
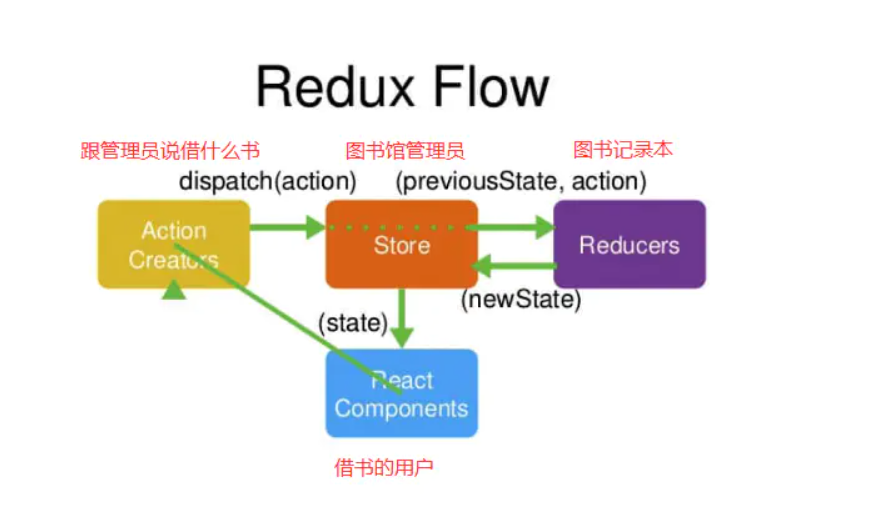
store、components、actionCreaters、reducers的关系即为:
首先有一个组件,组件要去获取store中的一些数据
actionCreaters通过dispatch(action)方法 让store知道 组件要获取数据
store在reducer查组件需要什么数据,reducer返回组件应该拿到的数据
store获得数据后把数据 返给 组件

为什么要Redux

Redux核心概念(3个)
action
默认是对象(同步action), {type: ‘xxx’, data: value}, 需要通过对应的actionCreator产生,
它的值也可以是函数(异步action), 需要引入redux-thunk才可以
reducer
根据老的state和指定的action, 返回一个新的state
不能修改老的state
store
redux最核心的管理对象
内部管理着: state和reducer
提供方法: getState(), dispatch(action), subscribe(listener)
createStore创建storestore.dispatch派发action,action传递给storestore.getState()获取store里面所有的数据内容store.subscribe()订阅store的改变,只要store发生改变,store.subscribe()中的回调函数就会执行
单个redux例子
基础 reducer store action
import { createStore } from 'redux'
/**
这是 reducer - a function describing "what happened"
- reducer = a current state value + an action object
- returns a new state value.
- 格式: (state, action) => newState
*
* The Redux state : plain JS objects, arrays, and primitives.
* The root state value is usually an object.
*/
function counterReducer(state = { value: 0 }, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return { value: state.value + 1 }
case 'DECREMENT':
return { value: state.value - 1 }
case 'RESET':
return { value: 0}
default:
return state
}
}
const store =createStore(counterReducer)
//查状态 0
console.log(store.getState());
//执行
store.dispatch({ type: "INCREMENT" })
store.dispatch({ type: "INCREMENT" })
store.dispatch({ type: "INCREMENT" })
//3
console.log(store.getState());
store.dispatch({ type: "DECREMENT" })
//2
console.log(store.getState());s
store.dispatch({ type: "RESET" })
//0
console.log(store.getState()); subscribe以及设置特殊值
//仓库放所有action 以及state
const initState = {
count :0 ,
list:['任务一',"任务二"]
};
//仓库放所有action 以及state
const store = createStore((state=initState,action)=>{
switch(action.type){
case "INCREMENT":
const incrementBy = typeof action.incrementBy ==='number'? action.incrementBy :1;
return { count:state.count+incrementBy }
case "DECREMENT":
const decrementBy = typeof action.decrementBy ==='number'? action.decrementBy :1;
return { count:state.count-decrementBy }
case "RESET": return { count:0 }
case "SET": return { count:action.count }
default: return state
}
})
//实时监控
const unsub=store.subscribe(()=>{ console.log(store.getState()); })
//执行
store.dispatch({ type: "INCREMENT", incrementBy:5})
store.dispatch({ type: "INCREMENT" })
store.dispatch({ type: "DECREMENT", decrementBy:3 })
store.dispatch({ type: "SET", count : 100 })
//直接取消掉subscribe
unsub();
//后面执行但是不会跟踪
store.dispatch({ type: "DECREMENT", decrementBy:3})
console.log(store.getState())利用解构 以及整理Action
const initState = {
count :0 ,
list:['任务一',"任务二"]
};
//仓库放所有action选择 以及state 以及返回新的对象
const store = createStore((state=initState,action)=>{
switch(action.type){
case "INCREMENT": return { count:state.count+action.incrementBy };
case "DECREMENT": return { count:state.count-action.decrementBy };
case "RESET": return { count:0 };
case "SET": return { count:action.count };
default: return state
}
})
//实时监控
const unsub=store.subscribe(()=>{ console.log(store.getState()); })
//返回操作函数(对象包装函数)
const increment =(payload={})=>{
return {
type: "INCREMENT",
incrementBy:typeof payload.incrementBy ==='number'? payload.incrementBy :1}
}
//这里利用解构 简化写法
const decrement =({decrementBy=1}={})=>{
return{ type: "DECREMENT", decrementBy}}
//执行
store.dispatch(increment({incrementBy:6}))
store.dispatch(increment({ type: "INCREMENT" }))
store.dispatch(decrement({decrementBy:5}))
store.dispatch({ type: "SET", count : 100})
//直接取消掉subscribe
unsub();
//后面执行但是不会跟踪
store.dispatch({ type: "DECREMENT", decrementBy:3})
console.log(store.getState())最终完整单个redux例子
最终得到基础的单个redux, 这里注意的重点是,我们用reducer 是为了通过得到一个state以及action 从而返回新的state,并没有改变原本的state,只是给了新的state
const initState = {
count :0 ,
list:['任务一',"任务二"]
};
const countReducer=(state=initState,action)=>{
switch(action.type){
case "INCREMENT": return { count:state.count+action.incrementBy };
case "DECREMENT": return { count:state.count-action.decrementBy };
case "RESET": return { count:0 };
case "SET": return { count:action.setCount };
default: return state
}
}
//仓库放所有action选择 以及state 以及返回新的对象
const store = createStore(countReducer)
//实时监控
const unsub=store.subscribe(()=>{ console.log(store.getState()); })
//返回操作函数(对象包装函数) action generator
const increment =(payload={})=>{
return {
type: "INCREMENT",
incrementBy:typeof payload.incrementBy ==='number'? payload.incrementBy :1}
}
//这里利用解构 简化写法
const decrement =({decrementBy=1}={})=>{
return{ type: "DECREMENT", decrementBy}
}
const reset =()=>{
return { type: "RESET" }
}
const set =({setCount}={})=>{
return { type: "SET", setCount}
}
//执行
store.dispatch(increment({incrementBy:6}))
store.dispatch(increment({type: "INCREMENT"}))
store.dispatch(decrement({decrementBy:5}))
store.dispatch(reset())
store.dispatch(decrement({decrementBy:5}))
store.dispatch(set({setCount:-99}))
//直接取消掉subscribe
unsub();
//后面执行但是不会跟踪
store.dispatch({ type: "DECREMENT", decrementBy:3 })
console.log(store.getState())多个reducer例子
那么接下来看看多个reducer的时候 处理数据怎么做
import {v4 as uuidv4} from 'uuid'
//两个数据例子
const demoState={
expenses:[{
id:'poijasdfhwer',
description:'January Rent',
note:'This was the final payment',
amount:54500,
createdAt:0
}],
filters:{
text:'rent',
sortBy:'amount',//date or amount
startDate:undefined,
endDate:undefined,
}
}
//default state & reducer
const expensesReducerDefaultState=[];
const expensesReducer=(state=expensesReducerDefaultState,action)=> {
switch(action.type){
case "ADD_EXPENSE":
//return state.concat(action.expense);//此处不影响原先数组 只是返回新数组
return [...state,action.expense];
case "REMOVE_EXPENSE":
return state.filter(function (elem) {
return (elem.id !== action.id);
});
case "EDIT_EXPENSE":
//return state.concat(action.expense);//此处不影响原先数组 只是返回新数组
return state.map((expense)=>{
if(expense.id===action.id){
return {
...expense,
...action.updates,
}
}else{
return expense
}
});
default: return state
}
}
//返回操作函数(对象包装函数) action generator
const addExpense=({
description="",
note="",
amount=0,
createdAt=0
}={})=>({
type:"ADD_EXPENSE",
expense:{
id:uuidv4(),
description,
note,
amount,
createdAt}
})
const removeExpense=({id}={})=>({ type:"REMOVE_EXPENSE", id })
const editExpense=(id,updates)=>({
type:"EDIT_EXPENSE",
id,
updates
})
//default state & reducer
const filtersReducerDefaultState={
text:'',
sortBy:'amount',//date or amount
startDate:undefined,
endDate:undefined,
};
const filtersReducer=(state=filtersReducerDefaultState,action)=> {
switch(action.type){
case "SET_TEXT_FILTER":
return {
...state,
text:action.name
}
default: return state
}
}
//action
const setTextFilter = (name)=>({
type:"SET_TEXT_FILTER",
name
})
//仓库放所有action选择 以及state 以及返回新的对象
const store = createStore(combineReducers({expenses:expensesReducer,filters:filtersReducer}))
//实时监控
const unsub=store.subscribe(()=>{ console.log(store.getState()); })
const expenseOne = store.dispatch(addExpense({description:"Rent",amount:1000}))
const expenseTwo = store.dispatch(addExpense({description:"Coffee",amount:666}))
store.dispatch(removeExpense({id:expenseOne.expense.id}))
store.dispatch(editExpense(expenseTwo.expense.id,{description:"RentNew",amount:19999}))
store.dispatch(setTextFilter("Rent")); 这里注意 对于箭头函数中,返回时对象,可以直接使用 ( )=>( {对象})
继续补充例子中的function
//default state & reducer
const expensesReducerDefaultState=[];
const expensesReducer=(state=expensesReducerDefaultState,action)=> {
switch(action.type){
case "ADD_EXPENSE":
//return state.concat(action.expense);//此处不影响原先数组 只是返回新数组
return [...state,action.expense];
case "REMOVE_EXPENSE":
return state.filter(function (elem) {
return (elem.id !== action.id);
});
case "EDIT_EXPENSE":
//return state.concat(action.expense);//此处不影响原先数组 只是返回新数组
return state.map((expense)=>{
if(expense.id===action.id){
return {
...expense,
...action.updates,
}
}else{
return expense
}
});
default: return state
}
}
//action
const addExpense=({
description="",
note="",
amount=0,
createdAt=0
}={})=>({
type:"ADD_EXPENSE",
expense:{
id:uuidv4(),
description,
note,
amount,
createdAt}
})
const removeExpense=({id}={})=>({ type:"REMOVE_EXPENSE", id })
const editExpense=(id,updates)=>({
type:"EDIT_EXPENSE",
id,
updates
})
const filtersReducerDefaultState={
text:'',
sortBy:'amount',//date or amount
startDate:undefined,
endDate:undefined,
};
const filtersReducer=(state=filtersReducerDefaultState,action)=> {
switch(action.type){
case "SET_TEXT_FILTER":
return {
...state,
text:action.name
}
case "SORT_BY_DATE":
return {
...state,
sortBy:'date'
}
case "SORT_BY_AMOUNT":
return {
...state,
sortBy:'amount'
}
case "SET_START_DATE":
return {
...state,
startDate:action.startDate
}
case "SET_END_DATE":
return {
...state,
endDate:action.endDate
}
default: return state
}
}
const setTextFilter = (name)=>({
type:"SET_TEXT_FILTER",
name
})
const sortByDate = ()=>({
type:"SORT_BY_DATE"
})
const sortByAmount = ()=>({
type:"SORT_BY_AMOUNT"
})
const setStartDate=(startDate)=>({
type:"SET_START_DATE",
startDate
})
const setEndDate=(endDate)=>({
type:"SET_END_DATE",
endDate
})
//仓库放所有action选择 以及state 以及返回新的对象
const store = createStore(combineReducers({expenses:expensesReducer,filters:filtersReducer}))
const getVisibleExpenses=(expenses,{text,sortBy,startDate,endDate})=>{
return expenses.filter((element)=>{
//if not set the startdate and createdAt is ok
const startDateMatch = typeof startDate !== 'number' || element.createdAt >= startDate;
const endDateMatch = typeof endDate !== 'number' || element.createdAt <= endDate;
const textMatch = element.description.toLowerCase().includes(text.toLowerCase());
return startDateMatch && endDateMatch && textMatch;
}).sort((a,b)=>{
if(sortBy === "date"){
return a.createdAt > b.createdAt ? 1 : -1;
}else if(sortBy === "amount"){
return a.amount > b.amount ? 1 : -1;
}
})
}
//实时监控
const unsub=store.subscribe(()=>{
const state=store.getState();
const visibleExpenses =getVisibleExpenses(state.expenses,state.filters);
console.log(visibleExpenses);
console.log(store.getState());
})
//返回操作函数(对象包装函数) action generator
const expenseOne = store.dispatch(addExpense({description:"cRent",amount:215610,createdAt:1000}))
const expenseTwo = store.dispatch(addExpense({description:"Coffee1",amount:1,createdAt:-1000}))
store.dispatch(addExpense({description:"Coffee2",amount:2,createdAt:2000}))
store.dispatch(addExpense({description:"Coffee3",amount:3,createdAt:3000}))
//store.dispatch(removeExpense({id:expenseOne.expense.id}))
store.dispatch(editExpense(expenseTwo.expense.id,{description:"c",amount:9}))
store.dispatch(setTextFilter("c"));
store.dispatch(sortByAmount());
//store.dispatch(sortByDate());
//store.dispatch(setStartDate(0));
//store.dispatch(setEndDate(999));
// const demoState={
// expenses:[{
// id:'poijasdfhwer',
// description:'January Rent',
// note:'This was the final payment',
// amount:54500,
// createdAt:0
// }],
// filters:{
// text:'rent',
// sortBy:'amount',//date or amount
// startDate:undefined,
// endDate:undefined,
// }
// }
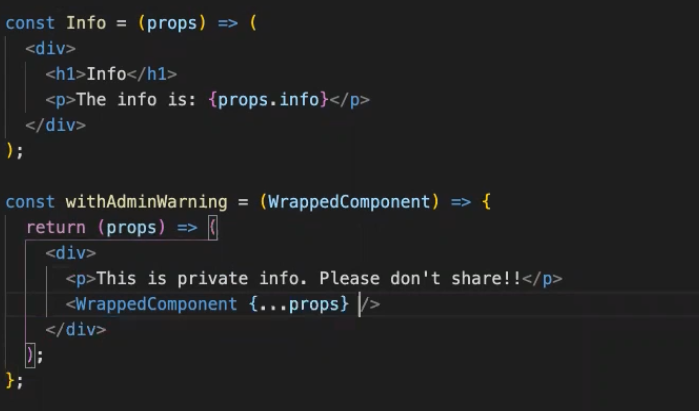
高阶组件(Higher-Order Components)
高阶组件就是一个函数,传给它一个组件,它返回一个新的组件
import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default (WrappedComponent) => {
class NewComponent extends Component {
// 可以做很多自定义逻辑
render () {
return <WrappedComponent />
}
}
return NewComponent
}例子

React Redux
Redux 跟 React 並沒有關係。你可以用 React、Angular、Ember、jQuery 或甚至原生 JavaScript 來撰寫 Redux 應用程式。
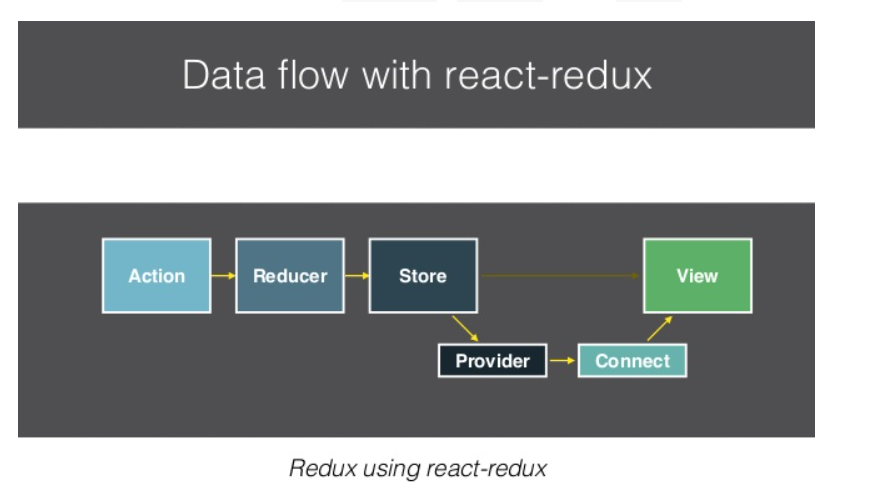
react-redux 是 React 和 Redux 间的桥梁,使用 Provider、connect 去连结 store 和 React View。
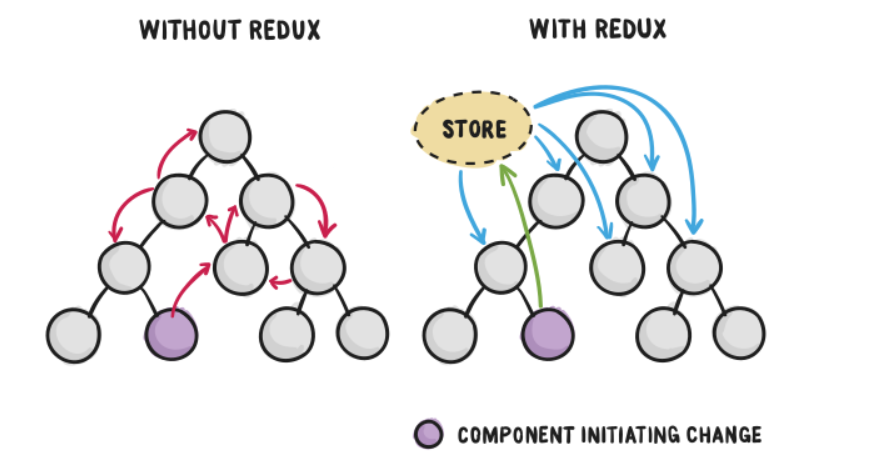
整合了 react-redux 后,我们的 React App 就可以解决传统跨 Component 之前传递 state 的问题和困难。只要通过 Provider 就可以让每个 React App 中的 Component 取用 store 中的 state,非常方便
Installation
npm install react-redux
yarn add react-reduxconnect方法的完整 API 如下
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
const VisibleTodoList = connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(TodoList)上面代码中,connect方法接受两个参数:mapStateToProps和mapDispatchToProps。它们定义了 UI 组件的业务逻辑。前者负责输入逻辑,即将state映射到 UI 组件的参数(props),后者负责输出逻辑,即将用户对 UI 组件的操作映射成 Action。
mapStateToProps函数
mapStateToProps是一个函数。它的作用就是像它的名字那样,建立一个从(外部的)state对象到(UI 组件的)props对象的映射关系。
作为函数,mapStateToProps执行后应该返回一个对象,里面的每一个键值对就是一个映射。请看下面的例子。
当 props接收到来自父组件一个小小的改动,那么你所使用的 ownProps 参数,mapStateToProps 都会被重新计算)。
mapStateToProps可以不传,如果不传,组件不会监听store的变化,也就是说Store的更新不会引起UI的更新
example:
const state = [];
// change code below this line
const mapStateToProps = (state)=>{
return {
messages: state
}
}
//或者
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
todoList: state.todoList
}
} 传入了props的:
const mapStateToProps = (state, ownProps) => {
return {
active: ownProps.filter === state.visibilityFilter
}
}mapDispatchToProps()
mapDispatchToProps是connect函数的第二个参数,用来建立 UI 组件的参数到store.dispatch方法的映射。也就是说,它定义了哪些用户的操作应该当作 Action,传给 Store。它可以是一个函数,也可以是一个对象。
如果mapDispatchToProps是一个函数,会得到dispatch和ownProps(容器组件的props对象)两个参数。
const mapDispatchToProps = (
dispatch,
ownProps
) => {
return {
onClick: () => {
dispatch({
type: 'SET_VISIBILITY_FILTER',
filter: ownProps.filter
});
}
};
}
//或者
//映射Redux actions到组件的属性
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch){
return{
onButtonClick:()=>dispatch(buttonClickAction),
onChangeText:()=>dispatch(changeTextAction)
}
}
//<button onClick={onButtonClick}>click me</button>Provider
React Redux provides <Provider />, which makes the Redux store available to the rest of your app
使用provider的例子
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import store from './store'
import App from './App'
const rootElement = document.getElementById('root')
const store = createStore(
combineReducers({
expenses:expensesReducer,
filters:filtersReducer
})
);
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
rootElement
)connect()
React Redux provides a connect function for you to connect your component to the store.
connect 返回的是函数,不是组件
使用connect例子1
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
const ExpenseList =(props)=>(
<div>
<h1>Expenses</h1>
{props.expenses.map((element)=>(
<ExpenseListItem key={element.id} {...element} />
))}
</div>
);
//将state中的信息取出来
const mapStateToProps = (state /*, ownProps*/) => {
return {
expenses: selectExpenses(state.expenses,state.filters),
filters:state.filters
}
}
//connect传递mapStateToProps数据给ExpenseList
const ConnectExpenseList= connect(mapStateToProps)(ExpenseList);
export default ConnectExpenseList使用connect例子 - input
import React from 'react'
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
import {setTextFilter} from '../actions/filters'
//直接绑定input
const ExpenseListFilters = (props)=>(
<div>
<input
type="text"
value={props.filters.text}
onChange={(e)=>{ props.dispatch(setTextFilter(e.target.value))
}}
/>
</div>
)
const mapStateToProps = (state /*, ownProps*/) => {
return {
filters:state.filters
}
}
//不用下面这种
//const ConnectExpenseList= connect(mapStateToProps)(ExpenseListFilters);
export default connect(mapStateToProps)(ExpenseListFilters) ;使用connect - 提交form
import React from 'react';
import ExpenseForm from './ExpenseForm'
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
import {addExpense} from '../actions/expenses'
const AddExpensePage =(props)=> {
return (
<div>
<p>Add Expense</p>
<ExpenseForm
onSubmit={(newExpense)=>{
props.dispatch(addExpense(newExpense))//这里相当于store.dispatch
}} />
</div>
)
}
export default connect()(AddExpensePage);//form本身,重点是要双向绑定 由于提交form 要用类元素
import React from 'react'
import moment from 'moment'
import "react-dates/initialize";
import "react-dates/lib/css/_datepicker.css";
import { SingleDatePicker } from "react-dates";
const now = moment();
console.log(now.format("Do, MMM YYYY"));
export default class ExpenseForm extends React.Component{
state={
description:'',
amount:'',
note:'',
createdAt:moment(),
canlendarFocused: false,
error:''
}
onDescriptionChange =(e)=>{
//console.log(e.target.value);
this.setState(state => ({
description: e.target.value
}));
}
onAmountChange=(e)=>{
//console.log(e.target.value);
this.setState(state => ({
amount: e.target.value
}));
}
onDateChange=(createdAt)=>{
if(createdAt){
this.setState({createdAt})
}
}
onFocusChange=({ focused }) => {this.setState({ canlendarFocused: focused })};
onNoteChange=(e)=>{
//console.log(e.target.value);
this.setState(state => ({
note: e.target.value
}));
}
//onsubmit的函数赋予input 从上级拿处理函数主体
onSubmit=(e)=>{
e.preventDefault();
if (!this.state.description || !this.state.amount) {
this.setState(() => ({
error: "Please provide description and amount!"
}));
} else {
console.log("submitting");
this.props.onSubmit({
description:this.state.description,
amount:parseFloat(this.state.amount,10)*100,
note:this.state.note,
createdAt:this.state.createdAt.valueOf()
})
}
}
//如果不想div,可以直接<>
render(){
return (
<div>
{this.state.error && <p>{this.state.error}</p>}
<form onSubmit={this.onSubmit}>
<input type="text" placeholder="Description" autoFocus value={this.state.description} onChange={this.onDescriptionChange} />
<input type="text" placeholder="Amount" value={this.state.amount} onChange={this.onAmountChange} />
{/* 此处用airbnb date pick */}
<SingleDatePicker
date={this.state.createdAt} // momentPropTypes.momentObj or null
onDateChange={this.onDateChange} // PropTypes.func.isRequired
focused={this.state.canlendarFocused} // PropTypes.bool
onFocusChange={this.onFocusChange} // PropTypes.func.isRequired
id="single_date_picker" // PropTypes.string.isRequired,
isOutsideRange={()=>false}//当前时间之前的也可以加入
numberOfMonths={1}//只显示一个月
/>
<textarea type="text" placeholder="add note if you need (optional)" value={this.state.note} onChange={this.onNoteChange} ></textarea>
<button>Add expense</button>
</form>
</div>
)
}
} 完整练习例子: expensifyApp indecisionApp counter
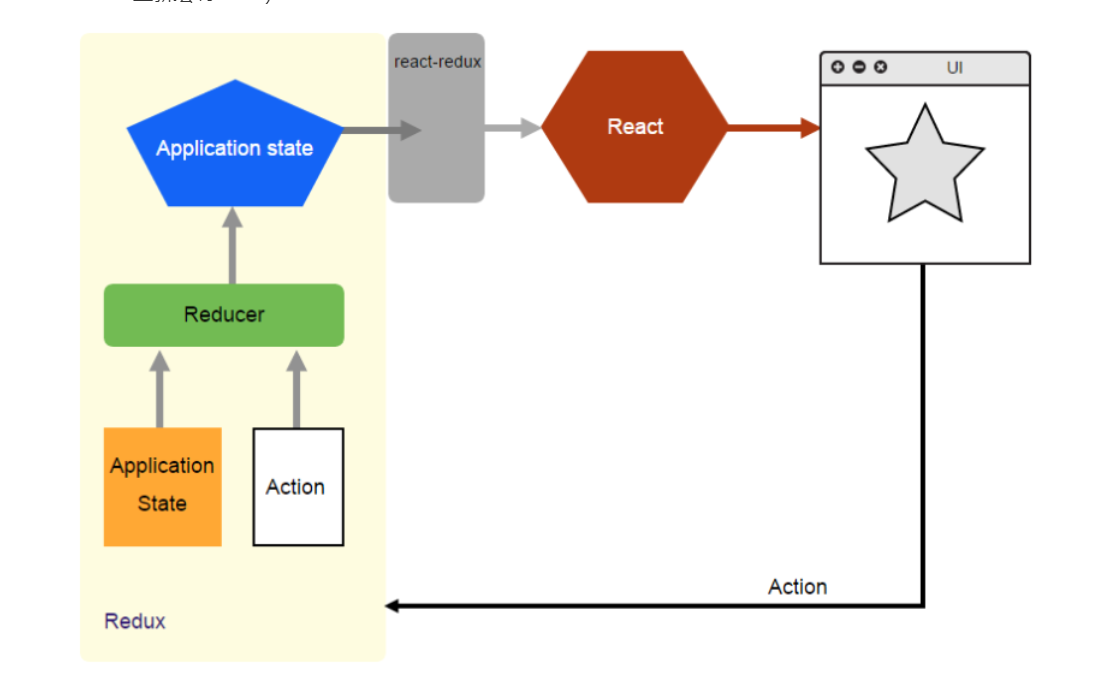
理解图:
改变obj属性
const defaultState = {
user: 'CamperBot',
status: 'offline',
friends: '732,982',
community: 'freeCodeCamp'
};
Object.assign({},state,{status:'online'} )tool
https://github.com/zalmoxisus/redux-devtools-extension
推荐读物
其他练习
Reference
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26347769/article/details/109634399
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903894082928654
https://chentsulin.github.io/redux/docs/basics/UsageWithReact.html
https://wizardforcel.gitbooks.io/reactjs101/content/Ch07/react-redux-real-world-example.html
https://medium.com/dailyjs/when-do-i-know-im-ready-for-redux-f34da253c85f

