React 开始
通过react的脚手架,创建项目进行开发,部署。(推荐)
全局安装create-react-app
$ npm install -g create-react-app创建一个项目
$ create-react-app your-app 注意命名方式React 事件与方法
通过前面的练习,我们将用class写
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
class IndecisionApp extends React.Component{
render(){
const title ='Indecision';
const subtitle = 'Put your life in the hand of Computer';
const options = ["option 1","option 2","option 3"]
return (
<div>
<Header title={title} subtitle={subtitle}/>
<Actions />
<Options optionArray={options}/>
<AddOption />
</div>
)
}
}
class Header extends React.Component{
render(){
return (
<div>
<h1>{this.props.title}</h1>
<h2>{this.props.subtitle}</h2>
</div>
)
}
}
class Actions extends React.Component{
handlePick(){
alert("pick!!!");
}
render(){
return (
<div>
{/* <p>This is Action</p> */}
<button onClick={this.handlePick} >What should I do</button>
</div>
)
}
}
class Options extends React.Component{
removeAll(){
alert("remove all ");
}
render(){
return (
<div>
Here are option Components from optionArray
{
(this.props.optionArray).map((option) => {
return <Option key={option} optionText={option}/>
})
}
<button onClick={this.removeAll}> Remove All</button>
</div>
)
}
}
class Option extends React.Component{
render(){
return (
<div>
{/* <p>This is Option Components</p> */}
<p>{this.props.optionText}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
//AddOption
class AddOption extends React.Component{
addOptionFunc(e){
e.preventDefault(); //防止刷新
const option = e.target.elements.option.value;//获得输入值
if(option){
console.log(option);
e.target.elements.option.value="";//清空输入值的显示
}
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<p>This is AddOption Components</p>
<form onSubmit={this.addOptionFunc}>
{/* name 用来取值*/}
<input type="text" name="option"/>
<button>+1</button>
</form>
</div>
)
}
}
/*
const title ='Indecision';
const subtitle = 'Put your life in the hand of Computer';
const options = ["option 1","option 2"]
const jxs = (
<div>
<Header title={title} subtitle={subtitle}/>
<Actions />
<Options optionArray={options}/>
<AddOption />
</div>
)
*/
//注意此处 const 与class 渲染的不同方式
//ReactDOM.render(jxs, document.getElementById('root'));
ReactDOM.render(<IndecisionApp />, document.getElementById('root'));事件绑定
原理解释
React事件绑定时需要注意this指向
react事件绑定时。this并不会指向当前DOM元素。往往使用bind来改变this指向。有参数就得使用bind
<button onClick={this.function.bind(this)}>Click Me</button>参考这篇文章:Choosing the Best Approach for React Event Handlers
1、function.bind()方式
2、inline arrow function方式
3、Class Property Arrow Functions - constructor
第一种方式比较常见,但因为每次父组件render时,会重新生成一个函数,相当于子组件的props发生了改变。子组件的PureComponent会失效。
第二种是一种性能好,书写简单,功能强大的方式。
第三种因为是类的属性,可能涉及到继承、方法调用问题,性能有影响。
接下来要加上动态事件,这时候跟前面的区别在于这里由于用的是class,属性之间没有办法很好的共享
function.bind()方式
const obj={
name="tom";
getName(){
return this,name;
}
}
//这里利用bind绑定对于后面的obj
const getName=obj,getName.bind({name:"joe"});
console.log(getName());inline arrow function方式
- 为事件提供的处理函数,必须是如下格式
onClick= { function } - 用的最多的事件绑定形式为:
<button onClick={ () => this.show('传参') }>按钮</button>
// 事件的处理函数,需要定义为 一个箭头函数,然后赋值给 函数名称
show = (arg1) => {
console.log('show方法' + arg1)
}回归例子
方式一 - bind
实际上我们尝试用处理removeAll, 先拿到所有的props,两种办法
//方法1:加上removeAll动态的事件,拿到如数的数据,方式一:绑定bind()
class Options extends React.Component{
removeAll(){
console.log(this.props.optionArray);
}
render(){
return (
<div>
Here are option Components from optionArray
{
(this.props.optionArray).map((option) => {
return <Option key={option} optionText={option}/>
})
}
{/* 绑定“参数对象”,所以这里绑定的实际上是传进来的props,所以函数操作对应就是参数对象 */}
<button onClick={this.removeAll.bind(this)}> Remove All</button>
</div>
)
}
}
缺点:
- 数量多时极其浪费内存
- 如果是子组件的props,则会导致子组件重新渲染
方式二 :通过constructor绑定
//方式二 通过constructor绑定
class Options extends React.Component{
constructor(props){//构造函数继承
super(props);
this.removeAll = this.removeAll.bind(this);
}
removeAll(){
console.log(this.props.optionArray);
}
render(){
return (
<div>
Here are option Components from optionArray
{
(this.props.optionArray).map((option) => {
return <Option key={option} optionText={option}/>
})
}
{/* 绑定“参数的this” */}
<button onClick={this.removeAll}> Remove All</button>
</div>
)
}
}方式三 箭头函数
State
组件自身的state,注意!!注意!! 这是对象
setState函数
做一个计数器中利用state进行改变数量
//利用算数函数 确保立即执行 保障同步性;因为setState本身是异步函数
incrementCount(){
this.setState((prevState, props) => ({
count: prevState.count + 1 //count 是state中属性
}));
this.setState((prevState, props) => ({
count: prevState.count + 1
}));
}
实际上不会,由于是异步,所以第一个设为0并没有完成,但是可能先+1;
实际例子
改变class内state变量
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
class Counter extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.addone=this.addone.bind(this);
this.minuseone=this.minuseone.bind(this);
this.reset=this.reset.bind(this);
this.state={ count:100 }
}
addone(){
this.setState((prevState)=>{
return {
count: prevState.count+1}
});
}
minuseone(){
this.setState((prevState)=>{
return {
count: prevState.count-1}
});
}
reset(){
this.setState((prevState)=>{
return {
count: 0}
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Count: {this.state.count} </h1>
<button onClick={this.addone }> +1</button>
<button onClick={this.minuseone}> -1</button>
<button onClick={this.reset}> reset</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render( <Counter />, document.getElementById('root'));setState 的三种写法
(1)对象
this.setState({key : value})
//或者
const new="newValue";
this.setState({new})(2)函数,一般是用于在setState之前做一些操作
this.setState(state=>{
return {key : value}
})
//或者
this.setState(
() => {
// TODO
console.log('')
return {
a:300
}
}
) (3)第二个参数,一般是用于在setState之后做一些操作
this.setState({
a:300
}, () => {
// TODO
console.log('state值修改成功,现在的name值为' + this.state.name)
})存在props值的修改state的值
因为更新的 props 和状态是异步的。这里,我们根据这些 props 更新状态。
// 错误方式
this.setState({
total: this.state.total + this.props.count,
})
// 正确方式
this.setState((state, props) => {
return {total: state.total + props.count}
})Props
默认props & 基本props
//默认input设置
const ShoppingCart = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<h1>Shopping Cart Component</h1>
</div>
)
};
ShoppingCart.defaultProps={items : 0}
//输入变量
const Items = (props) => {
return <h1>Current Quantity of Items in Cart: {props.quantity}</h1>
}
Items.defaultProps = { quantity: 0 }
class ShoppingCart extends React.Component {
constructor(props) { super(props); }
render() {
return <Items quantity={ 10 }/>
}
};
//数组
<ChildComponent colors={["green", "blue", "red"]} />
props 输入限制
componentName.propTypes = {
inputName: PropTypes.string.isRequired//string
};
componentName.propTypes = {
inputName: PropTypes.number.isRequired//number
};
Props children
this.props.children。它表示组件所有的子节点。
this.props.children 的值有三种可能:
- 如果当前组件没有子节点,它就是 undefined;
- 如果有一个子节点,数据类型是 object;
- 如果有多个子节点,数据类型就是 array
基本语法
一个 span 标签在 Parent 中作为Child的子节点传入,可在 Child 中通过 this.props.children 取到:
class Parent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Child>
<div>slot1</div>
<div>slot2</div>
<div>slot3</div>
</Child>
)
}
}
class Child extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>{this.props.children[2]}</div>
<div>{this.props.children[1]}</div>
<div>{this.props.children[0]}</div>
</div>
)
}
}React.Children 方法
React 提供了工具方法 React.Children 来处理 this.props.children。
- React.Children.map
object React.Children.map(object children, function fn)遍历 props.children ,在每一个子节点上调用 fn 函数。
- React.Children.forEach
React.Children.forEach(object children, function fn)类似于 React.Children.map(),但是不返回对象。
- React.Children.count
number React.Children.count(object children)返回 children 当中的组件总数。
- React.Children.only
object React.Children.only(object children)返回 children 中仅有的子节点。如果在 props.children 传入多个子节点,将会抛出异常。
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script src="common/react.js"></script>
<script src="common/react-dom.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/babel-core/5.8.38/browser.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return <div>
{/*props.children获取下面4个子节点:3个元素节点和1个文字节点*/}
{this.props.children.map((item,index)=> <p key={index}>{item}</p>)}
</div>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<App>
{/*加一些子元素*/}
<span>rick</span>
<span>zhangamie</span>
<span>react</span>
2132132
</App>,
document.getElementById('app')
)
</script>
</body>
</html>Props vs State
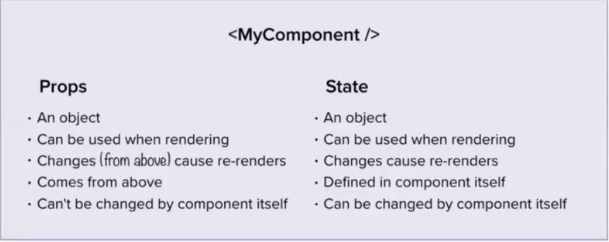
props是单向联动的
函数组件-函数名称以大写字母开头
无状态组件
无状态组件不支持this!!
/* 基本语法
const User=()=>{
return <div></div>
}*/
//这里不需要用this.props
const User=(props)=>{
return (<div>
<p>Name: {props.name}</p>
<p>Age: {props.age}</p>
</div>)
}
ReactDOM.render( <User name="tom" age={28}/>, document.getElementById('root')); class组件 const组件对比
//注意区别 仔细看对比
class Header extends React.Component{
render(){
return (
<div>
<h1>{this.props.title}</h1>
<h2>{this.props.subtitle}</h2>
</div>
)
}
}
const Header=(props)=>{
return(
<div>
<h1>{props.title}</h1>
<h2>{props.subtitle}</h2>
</div>
);
}默认input
const Header=(props)=>{
return(
<div>
<h1>{props.title}</h1>
<h2>{props.subtitle}</h2>
</div>
);
}
//此处为默认input
//className.defaultProps={ 属性:''}
Header.defaultProps={
title:'Default Title'
}
class IndecisionApp extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state={
options : props.options
}
this.handlePick=this.handlePick.bind(this);
this.removeAll=this.removeAll.bind(this);
}
render(){
const title ='Indecision App';
const subtitle = 'Put your life in the hand of Computer';
return (
<div>
{/* 此时title就是默认的title
<Header title={title} subtitle={subtitle}/>
*/}
<Header subtitle={subtitle}/>
</div>
)
}
}
IndecisionApp.defaultProps={ option:[]}
//有无输入区别
ReactDOM.render(<IndecisionApp />, document.getElementById('root'));
//ReactDOM.render(<IndecisionApp options={["option 1","option 2"]} />, document.getElementById('root'));input双向绑定
class ControlledInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
input: ''
};
this.handleChange=this.handleChange.bind(this);
}
handleChange(event){
this.setState( {
input: event.target.value,
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{ /* 这里注意: 不仅input输入变状态 状态的改变也会改变输入*/}
<input type="text" value = {this.state.input} onChange={this.handleChange} />
<h4>Controlled Input : </h4>
<p>{this.state.input}</p>
</div>
);
}
};onclick函数
const Option = (props)=>{
return(
<div>
<p>{props.optionText}</p>
<button onClick={()=>{props.deleteFunc(props.inputText)}}>remove this</button>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>Click Me</button>{/*handleClick是函数*/}
</div>
)
}状态组件
class StatefulComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: ""
}
}
render() {
//或者可以这里有个const 拿到上面的state中的值,下面再次调取
return (
<div>
<h1>{this.state.name}</h1>
</div>
);
}
};父子组件之间的传递以及实例
单纯的input传输(子组件input给父)
class MyApp extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
inputValue: ''
}
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
}
handleChange(event) {
this.setState({
inputValue: event.target.value
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<GetInput input={this.state.inputValue} handleChange={this.handleChange}/>
<RenderInput input={this.state.inputValue}/>
</div>
);
}
};
class GetInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>Get Input:</h3>
<input
value={this.props.input}
onChange={this.props.handleChange}/>
</div>
);
}
};
class RenderInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>Input Render:</h3>
<p>{this.props.input}</p>
</div>
);
}
};子组件事件 影响父组件state
父组件 - IndecisionApp
class IndecisionApp extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state={
options : ["option 1","option 2","option 3"],//options : [ ]
pickedOption:null,
}
}
handleRemove=(optionValue)=>{
console.log("remove this ",optionValue);
this.setState(()=>({
options: this.state.options.filter(function (elem, index, arr) {
return elem !== optionValue
})
}))
}
render(){
const subtitle = 'Put your life in the hands of a computer'
return(
<div>
<Header subtitle={subtitle}/>
{/* What should i do render pick- 弹窗+产生随机数 */}
<Action active={this.state.options.length} hanldPickOption={this.hanldPickOption} />
{/* show all options+ remove all + remove one */}
<Options options={this.state.options} removeAll={this.handleRemoveAll} remove={this.handleRemove}/>
{/* add one option */}
<AddOption addOption={this.handleAddOption}/>
{/* 弹框 */}
<OptionModal pickedOption={this.state.pickedOption} clearPickedOption={this.clearPickedOption} />
</div>
)
}
}子组件 - Options
const Options = (props)=>{
return (
<div>
{props.options.length === 0 && <p>Add an option to started!</p>}
<ul>
{/* {props.options.map((i) => <li key={i}>{i} <button onClick={props.remove}> remove </button></li>)} */}
{props.options.map((e,i) => <Option key={e} optionText={e} remove={props.remove}/>)}
</ul>
<button onClick={props.removeAll}>Remove all</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Options子组件向父组件通信
子组件通过 回调函数 向父组件传递数据。父组件将自己的某个方法传递给子组件,子组件通过this.props接收到父组件的方法后进行调用。
如果子组件内需要修改父组件传递过来的数据,需要通过调用父组件的方法,在父组件中对数据进行修改。
import React, { Component ,createRef} from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
//子组件
class Child extends Component{
state={
name:"admin",
age:18
}
childClickHandle=()=>{
this.props.showInfo({address:"beijing"})
}
render(){
return (
<div>
{/*方式一:直接调用父组件的方法*/}
<button onClick={this.props.showInfo.bind(this,this.state)}>按钮</button>
{/*方式二:先调用自身的方法,再调用父组件的方法*/}
<button onClick={this.childClickHandle}>按钮</button>
</div>
)
}
}
//父组件
class Parent extends Component{
clickHandle(data){
//data为子组件中传递过来的数据
//{address: "beijing"}
//{name: "admin", age: 18, sex: "woman"}
console.log(data);
}
render(){
return <Child showInfo={this.clickHandle.bind(this)}></Child>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Parent/>,
document.getElementById('root')
);reference:
- https://blog.csdn.net/u012372720/article/details/94000150
- CodeCamp 练习题
- React 组件通信的五种方式_props_ref_Context_Redux

